 |
| Image by - shutterstock.com |
Journal
Or
Journal in Accounting
Or
Journal in Bookkeeping
Introduction
Everyday businessmen perform large number of transactions. These
transactions cannot be remembered at a glance. Therefore these transactions
must be recorded in different types of books. He keeps different accounting
records. The number of books depends upon the size and nature of business and
volume of transactions but important books of accounts which must be maintained
by every business men are Journal and Ledger.
Journal is a book employed to classify or sort out transaction in a form
convenient for their subsequent entries in Ledger Journal keeps record of daily
financial transaction. It is also known as Book of Original Entry. When the
Journal transactions are recorded in the Journal it becomes Journal entry.
Journal entries consist of the name of debit and name of credit involved
in the financial transaction with a brief narration. Journal is a book in which
the business transactions are first recorded in a chronological order i.e. Date
wise in the order in which they take place. Generally the different types of
Books of Accounts are maintained by a businessman for recording the business
transactions.
He maintains primary books and secondary books, Primary books include
Journal proper and special Journal which includes Purchases Books, Sales Book,
Purchase Return Book, Sales Return Book, Bills Receivable Book, Bills Payable
Book and Secondary Book includes Journal Ledger.
Related Articles
👆 Financial Accounting
👆 Types of Accounting
👆 Cost Accounting
👆 Types of Cost Accounting
👆 Methods and Techniques of Costing
👆 Cost Sheet
👆 Cost Management
👆 Cost Control and Reduction
👆 Cost Accounting System
👆 Difference between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
👆 Management Accounting
👆 Materials Control
👆 Bookkeeping
👆 Accounting methods
👆 Accounting Terminologies
👆 Double Entry System
👆 Classification of Accounts
Meaning
The word “Journal” is derived from the French word “JOUR” which means a
“Day”. Therefore journal means a “daily record”. A journal contains a daily
record of business transactions and hence it has been named so, as soon as a
transaction takes place its debit and credit aspects are analyzed and first of
all recorded chronologically i.e. In the order of their occurrence(taking
place). Journal is a book of original entry or primary entry.
Definition
According to L.C.Cropper “A journal is a book, employed to
classify or sort out transactions in a form convenient for their subsequent
entry in the Ledger”
According to a Dictionary for Accountant written by Eric Kohler “
A Journal is the book of original entry are recorded transaction not provided
for in specialised journals”.
Importance and utility of Journal
Journal is an important book in Book-keeping. All business
organisations, keep the Journal. The importance and utility is as follows:-
This is the principal book of account. It includes all types of accounts
of business.
It shows all necessary information regarding transactions.
The Journal has date wise record of all the transactions with details
about accounts it helps to understand the events when its took place.
The Journal is subsidiary book in which all the day to day transactions
are recorded first in chronological order in debit and credit form and with the
amount of each transaction.
Accounting procedure is followed on the basis of accounting documents.
The narration provides a brief explanation about the transactions .It
helps to increase the clarity of every transaction.
It helps to find and prevent errors.
It helps to check arithmetical accuracy of the transactions.
It helps in preparation of Final Accounts.
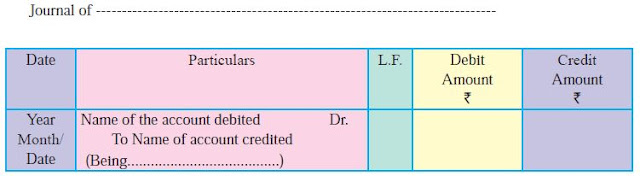
Format/ Ruling/ Performa of Journal
Explanation of Columns
Date: In this column of Journal records of the
year, month and date of every transaction is written. The year should be
written at the top and below that the month and date should be written.
Debit A/c: It records the name of the account to be debited.
Credit A/c: It records the name of the account to be
credited.
This is decided by applying the rules of Debit and Credit. The account
to be debited is always written first. The word “Dr” is written in front of
debited account just near L.F. Column. The account to be credited is written on
the next line beginning with the word “To” after leaving short space just near
date column. Narration is to be written just below the journal entry.
Narration: After each entry, a brief explanation of the
transaction together with necessary details is given in the particulars column
with in brackets called narration. The words ‘For’ or ‘Being’ are used before
starting to write down narration. Now, it is not necessary to use the word
‘For’ or ‘Being’.
Ledger Folio Number: It means page number of the ledger. The transaction
entered in the journal is posted to the Ledger. In this column the page number should
be recorded against each and every account at the time of posting in ledger.
The Folio number may be written in ‘red ink’ to distinguish them from the
amount.
Debit Amount: In this column the amount of debit account is
written.
Credit Amount: In this column the amount of credit account
is written.
Casting of Journal
At the end of each page of Journal, the total of debit amount and credit
amount column is taken to check arithmetical accuracy of the transaction. The
totals of both the columns must be equal.
After recording Journal Entries, at the end of each page the total of
amount columns is carried forward to the next page by writing the words Total
c/f in particulars column. The next page will begin with the total brought
forward from previous page, by writing the words Total b/f, on the last page of
journal ‘Grand Total’ is casting.
Journalising
The process of entering or recording the transaction in a Journal is
called as journalising.
Steps in Journalising
The process of analysing the business transactions under the heads of
debit and credit and recording them in the Journal is called
Step 1
Determine the two accounts which are involved in the transaction.
Step 2
Classify the above two accounts under Personal, Real or Nominal.
Step 3
Find out the rules of debit and credit for the above two accounts.
Step 4
Identify which account is to be debited and which account
is to be credited.
Step 5
Record the date of transaction in the date column. The year
and month is written once, till they change. The sequence of the dates and
months should be strictly maintained.
Step 6
Enter the name of the account to be debited in the particulars
column very close to the left hand side of the particulars column followed by
the abbreviation Dr. in the same line. Against this, the amount to be debited
is written in the debit amount column in the same line.
Step 7
Write the name of the account to be credited in the
second line starts with the word ‘To’ a few space away from the margin in the
particulars column. Against this, the amount to be credited is written in the
credit amount column in the same line.
Step 8
Write the narration within brackets in the next line in
the particulars column.
Step 9
Draw a line across the entire particulars column to separate
one journal entry from the other.
How transaction travels
Example 1: Purchased Laptop from Peter & Company worth 50,000 at 18% GST and amount paid by cheque
Cost of Laptop = 50,000
Add:CGST 9% = 4,500
SGST 9% = 4,500
Net value = 59,000
More Related Articles
👆Option Trading in India
👆Option Trading Greeks
👆How to calculate option price (Options Pricing)
👆Options Trading Strategies India
👆Options Trading Strategies Long Call
👆Options Trading Strategies Long Put
👆Options Trading Strategies Short Call
👆Options Trading Strategies Short Put
👆Options Trading Strategies Collar
👆Options Trading Strategies Bull Call Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bull Put Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bear Call Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bear Put Spread
Writing
of Journal Entries
Simple Journal Entry: In a simple entry, only two accounts are affected, one account is
debited and the other is credited. Few transactions are given below for Simple
Journal Entries.
Combined Journal Entry: In many of transactions ,more than two accounts are affected . A
Journal Entry which contains more than one debit or more than one credit or
both is called as a combined /compound Journal Entry.
Thus, in a combined Journal Entry.
Several accounts are debited and one account is credited.
One account is debited and several accounts are credited.
More than one account is debited and more than one account is credited.










No comments:
Post a Comment