 |
| Image by - shutterstock.com |
Ledger
Or
General
Ledger
Or
Ledger
in Accounting
Introduction
In the process of accounting, all the business transactions are recorded
in chronological order in Journal. These business transactions are recorded in
proper books of accounts.
Books of Accounts
Journal or Subsidiary Books
(Books of Original/Primary entry)
Ledger
(Book of Final/Secondary entry)
At the end of the particular period if we want to know what is the total
amount spent on particular type of expense, or what is the amount payable to
particular person /party? These types of questions cannot be answered easily
through Journal. So to overcome these limitations of Journal we need Ledger. A
Ledger is called as the main Book of Accounts. Once the transactions are
recorded in Journal or Subsidiary books the next stage is the transfer of those
transactions in their respective accounts opened in the Ledger.
Meaning of Ledger
Ledger is the Principal Book of accounts. It is also called as book of
final entry. It is summarised record which contains all the accounts e.g.
Assets A/c, Liabilities A/c, Capital A/c, Revenue A/c, Expenses A/c.
Accounting Related Articles
👆 Financial Accounting
👆 Types of Accounting
👆 Cost Accounting
👆 Types of Cost Accounting
👆 Methods and Techniques of Costing
👆 Cost Sheet
👆 Cost Management
👆 Cost Control and Reduction
👆 Cost Accounting System
👆 Difference between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
👆 Management Accounting
👆 Materials Control
👆 Bookkeeping
👆 Accounting methods
👆 Accounting Terminologies
👆 Double Entry System
👆 Classification of Accounts
Definitions of Ledger
The word ‘LEDGER’ is derived from Latin word ‘Ledger’ which
means ‘to contain’ As the ledger is the collection of all the accounts so ‘it
contains’ and hence the name signifies.
“ A Ledger Account may be defined as a summary, statement of all the
transactions relating to persons, assets, expenses or incomes which have taken
place during a given period to time and shows their net effect”.- S. P.
Jain, K. L. Narang –Advanced Accountancy.
“Main record of the accounts of a business, traditionally, a ledger was
a large book with separate pages for each account. In modern systems ledger may
consist of separate cards or computer records’- Oxford Dictionary.
“ A Ledger containing accounts in which all the transactions of a
business enterprises or other accounting units are classified either in detail
or in summary form”- E. L. Kohler- A Dictionary for Accountants.
Importance
of Ledger
It is the summarised record of all the transactions in form of Asset
A/c, Liabilities A/c, Expenses A/c, Income A/c etc.
The ultimate object of Book-Keeping is to ascertain with the least
trouble, what the amount is owed to the supplier, what is the amount receivable
from the customer and so on. In the process of posting information collected is
condensed in form of Debtors A/c, Creditors A/c to get the ready results.
It is necessary for preparation of Trial Balance.
The financial position of the business can be easily known with the help
of various types of Assets A/c and Liabilities A/c.
It is possible to prepare various types of income statement on the basis
of balances shown by different ledger Accounts.
Ledger can be used as a control tool as it shows accounts of various
expenses with the balance.
On the basis of the results shown in the Ledger it is useful for the
management to forecast or plan the future plan of action.
Contents
of Ledger
Ledger is a bound book which contains several pages. Each page of a ledger is serially numbered. For each account separate page is allotted. The page number of the ledger is called as 'Ledger Folio' (L.F.) Each ledger account is divided into two sides. The left side is known as debit side and the right side is known as credit side. This is indicated by writing the abbreviations ‘Dr.’ on the left side top corner and ‘Cr.’ on the right side top corner.
Every Ledger has an index. Index is prepared in the alphabetical order.
The page number on which a particular account appears is shown against the name
of the account shown in index. This facilitates quick reference.
Both the sides of the ledger have four columns. These columns are:-
Date: In this column the date of the transaction is
written. The year, month and date should be clearly mentioned.
Particulars: In this column, the name of the account in
which the corresponding credit or debit is found under double entry principle
will be mentioned. The posting on the debit side begins with ‘To’ and on the
credit side with ’By’.
Journal Folio (J.F.): Folio means page number. In Journal Folio
(J.F.) column, page number of journal from where we have transferred the entry
into Ledger is to be written.
Amount: In the column, the amount for which an
account is debited or credited is entered.
Specimen/Format/Performa
of Ledger
Specimen of the
ledger in ‘T’ form is given below:
Posting
of entries from Journal/Subsidiary books to Ledger
Transactions are recorded in various books of original entry as and when
they occur. From the books of original entry, the necessary records in the
Ledger are made. The process of transferring entries from the Journal or
Subsidiary Books into the appropriate account in the Ledger is called 'Posting'.
The Recording process:
The process of recording transactions in the Ledger involves the
following steps:
From the Journal entries, ledger posting is to be done.
Open the necessary ledger accounts with proper headings.
If the opening balance of ledger account is given , it should be posted
first, either as ‘To balance b/d’ or ‘By balance b/d’
For posting the transactions into the ledger account, first write the
date of the transaction in the date column.
In the particular column on the debit side of the ledger account the
name of the account credited in the entry is written and on the credit side of
ledger account, the name of the account to be debited in the entry is written.
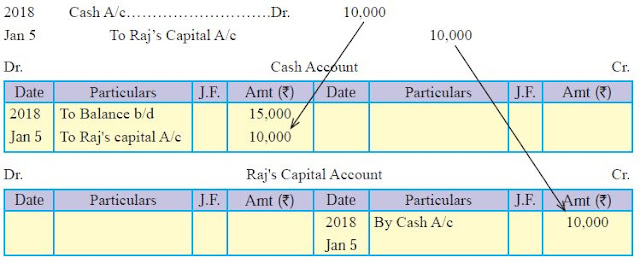
Example
The above process of recording transactions can be studied with the help
of following example;
Balance of Cash on 1st January 2018 15,000
On 5th January 2018 Raj invested 10,000 in
the business.
The Journal Entry for the transaction would
be
Posting
of entries from Journal Proper
The entries shown in Journal Proper are posted to respective accounts in
the Ledger.
Balancing
of Ledger Accounts
Balancing of Ledger accounts means totaling both the sides of Ledger
Account, finding the difference between greater total and smaller total and
recording the difference on the smaller side.
Steps for balancing the ledger accounts
Take the totals of both the sides’ i.e Debit and Credit.
Find out the difference between both the sides.
If the debit side total is more than the credit side then difference
will be shown on credit side as ‘By Balance c/d’ in particulars column and
difference amount is shown in amount column.
Same way if the credit side total is higher than the debit side total
then the difference amount is shown on debit side as ‘To Balance c/d’ in
particulars column and difference amount is shown in amount column.
These closing balances of different ledger accounts are shown as Opening
Balances for the next period. Closing balance shown on debit side of ledger
account will be shown as Opening Balance on the credit side at the beginning of
the period as ‘By Balance b/d’
Closing Balance shown on credit side of ledger account will be shown on
debit side of the account as Opening Balance at the beginning of the period as ‘To
Balance b/d’
Note: If the total of debit side of the account is higher than the total
of credit side the account is said to have Debit balance and vice-versa.
Stock Market Related Articles
👆Option Trading in India
👆Option Trading Greeks
👆How to calculate option price (Options Pricing)
👆Options Trading Strategies India
👆Options Trading Strategies Long Call
👆Options Trading Strategies Long Put
👆Options Trading Strategies Short Call
👆Options Trading Strategies Short Put
👆Options Trading Strategies Collar
👆Options Trading Strategies Bull Call Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bull Put Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bear Call Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bear Put Spread
Balancing of Ledger Accounts
Personal Account
Real Account
Nominal Account
Balancing of Personal Account
These accounts may have debit balance or credit balance or nil balance.
A personal account having debit balance is a Debtor and credit balance is a
Creditor. Balance of these accounts is carried forward.
Debit balance: If the debit side total of ledger Account is
more than the credit side total it indicates a debit balance.
Credit balance: If the total of credit side of an account is
more than debit side it indicates credit balance.
Balancing of Real Account
Accounts which are related to assets and properties are real accounts.
e.g.: Cash A/c, Furniture A/c etc. Real Account always shows a debit balance.
Balancing of Nominal Account
Nominal Accounts means the accounts which are related to expenses, incomes, losses and gains. This account may have a debit balance or a credit balance. At the end of the accounting year the balances of all Nominal Accounts are transferred to Trading or Profit and Loss Account.









No comments:
Post a Comment