 |
| Image by - Pixabay.Com |
Covered
Call
A covered call position is
created by buying (or owning) stock and selling call options on a
share-for-share basis. In the example, 100 shares are purchased (or owned) and
one call is sold. In return for the call premium received, which provides
income in sideways markets and limited protection in declining markets, the
investor is giving up profit potential above the strike price of the call. The
call premium increases income in neutral markets, but the seller of a call
assumes the obligation of selling the stock at the strike price at any time
until the expiration date.
In a covered call position,
the risk of loss is on the downside. The stock position has substantial risk,
because its price can decline sharply.
Stock Market Related Articles
👆Option Trading in India
👆Option Trading Greeks
👆How to calculate option price (Options Pricing)
👆Options Trading Strategies India
👆Options Trading Strategies Long Call
👆Options Trading Strategies Long Put
👆Options Trading Strategies Short Call
👆Options Trading Strategies Short Put
👆Options Trading Strategies Collar
👆Options Trading Strategies Bull Call Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bull Put Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bear Call Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Bear Put Spread
👆Options Trading Strategies Synthetic Long Call
Mr. G owns Reliance Shares
and expects the price to rise in the near future. Mr. G is entitled to receive dividends
for the shares he hold in cash market.
Covered Call Strategy
involves selling of OTM Call Option of the same underlying asset. The OTM Call
Option Strike Price will generally be the price, where Mr. G will look to get
out of the stock. He will receive premium amount from writing the Call option.
Risk: Mr. G will incur losses on
his short position when the stock moves beyond the strike price of the call written.
This strategy is generally adopted by the people who are ‘Neutral or Moderately
Bullish’ on the underlying asset.
Reward: Mr. G will make profits
when the stock price shoots up and pockets the premium which he received from
shorting the Call Option. If it comes down then he is willing to exit at a point,
the exit point is where Mr. G has shorted the Call Option.
Breakeven
Point
is Stock price minus call premium received
Action
Buy Shares in Cash/Future
Sell
OTM Call Option
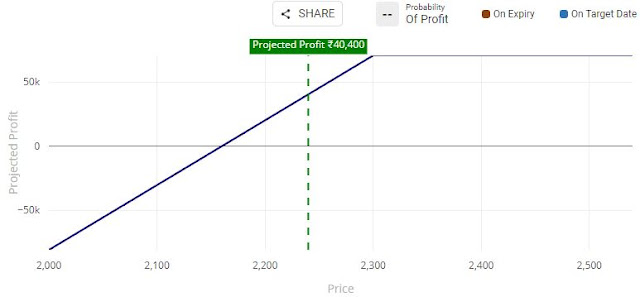
Example
RIL is trading around Rs 2240
levels. Lot size of RIL Option is 505. Mr. G is bullish in nature and buys one
lot of RIL @ Rs 2240 from the market. He also shorts one 2300 strike Call
Option for a premium of Rs. 80.
 |
| Image by - sensibull.com |
Breakeven Point Breakeven Point is 2,160 (2240-80).
Image by - sensibull.com
Result 1: If RIL closes at Rs. 2240, Mr.
G will received from call writing it i.e. Rs.40,400 (80*505).
 |
| Image by - sensibull.com |
Result 2: If RIL closes at Rs. 2300, Mr. G will make a profit on his long position in future market and profit on his short call. His net payoff will be Rs. 70,700.
Image by - sensibull.com
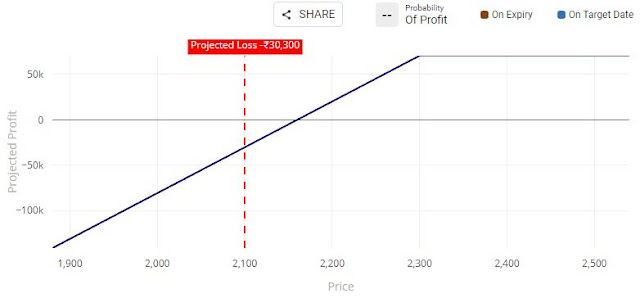
Result 3: If RIL closes at Rs. 2100, Mr. G will make a loss on his long position in future market and profit on his short call. His net loss will be Rs.30,300.








No comments:
Post a Comment